|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rhythm is timing patterns among syllables.
There are basically two types of sentence rhythm in languages:
"stress-timed rhythm" and "syllables-timed rhythm."
|
|
(A) Stress-timed Rhythm |
(B) Syllable-timed Rhythm |
 |
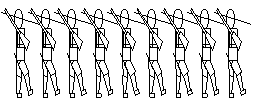 |
|
Question:
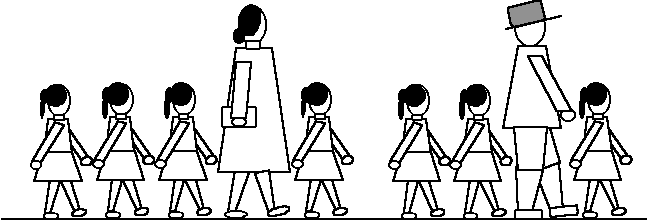
Which picture represents English speech rhythm?
Are there stressed syllables in that sentence?
The question is easy, right? Did you get the answer - pictures (A)?
In picture (A), 2 adults represent the stressed syllable, while 7 children
represent
unstressed
syllables in the sentence "pronunciation
is important."
The stressed and unstressed
syllables go together to make up the English speech rhythm.
|
| top |
|
Do you know which words in English sentences are stressed and which are not?
Basically
words can be divided into two categories: content
words and structure
words.
Content words are those which carry the basic meaning of a sentence, such
as nouns and verbs. Structure words, also called function words, show
grammatical
relationship, such as pronouns and prepositions. In
general, content
words need to emphasized, while structure
words are usually
de-emphasized
and reduced.
The following chart will help you know the rules better.
|
|
Content words (emphasized) |
Structure words (de-emphasized) |
|
nouns (cat,
book, Mary)
|
pronouns
(he, she, it, they)
|
|
Negative
words and
negative
"to-be," "to-have," and auxiliary verbs need to be stressed.
|
| top |
|
top |
|
(A) Oh, I thought you
wanted coffee.
|
|
|
(A) So it's not her
knee.
|
|
|
(A) Whose book then?
|
|
|
(A) You thought she
was inside?
|
| top |
We usually pause
1. before punctuation marks
( , . ; : ? ! )
2. before conjunctions
(and, or, but, which, that, since...)
3. between grammatical units such as phrases,
clauses, and sentences.
Look at the following example.
Try to read this passage with me.
| top |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|